Clinically Reviewed by
Assistant Professor & Tele-Rehabilitation In-Charge (SLP), MERF-ISH
Cochlear implants (CIs) have transformed the lives of children with hearing loss, enabling them to perceive sound and engage with their environments. However, the journey to effective communication and language development for these children is often complex and ongoing. Teletherapy, a remote therapeutic approach leveraging digital technology, is emerging as a powerful tool in supporting children with cochlear implants and their families. This blog explores how teletherapy enhances outcomes for children with cochlear implants, discussing its benefits, implementation strategies, and the future of this innovative approach.
Understanding Cochlear Implants
Cochlear Implants: Restoring Sound, Transforming Lives
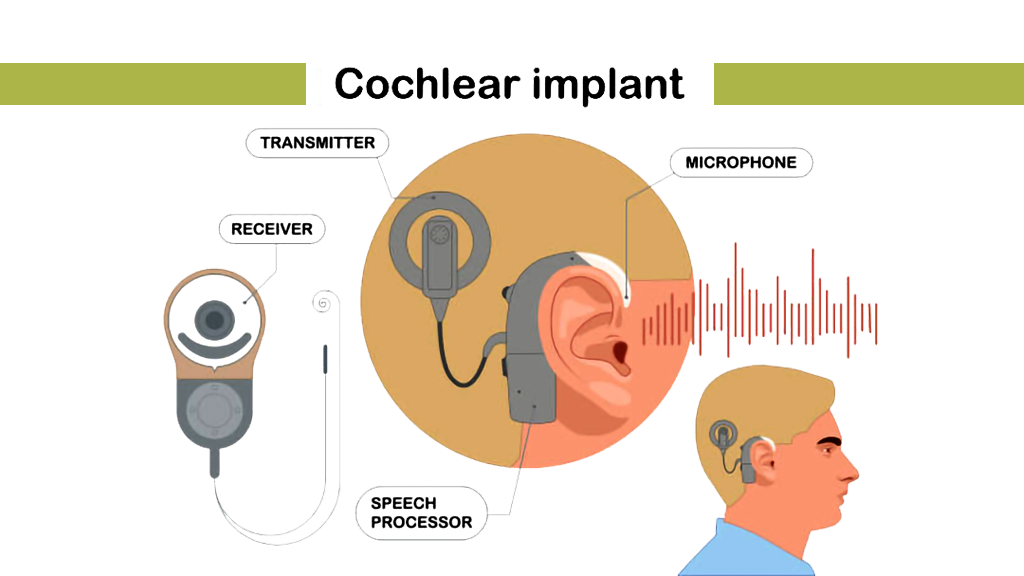
Cochlear implants are medical devices that bypass damaged inner ear cells to directly stimulate the auditory nerve, helping those with severe hearing loss. They consist of an external sound processor that captures and converts sound into digital signals and an internal electrode array placed in the cochlea, which sends these signals to the auditory nerve, enabling the brain to perceive sound. Unlike hearing aids, which amplify sound, cochlear implants provide direct auditory input for individuals with profound hearing loss.
Key Components of Cochlear Implants:
- External Processor: Worn behind the ear, it captures and processes sound.
- Internal Implant: Surgically placed under the skin, it converts signals into electrical impulses and stimulates the auditory nerve.
- Electrodes: Inserted into the cochlea, they deliver the electrical impulses to the auditory nerve.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is critical for children with hearing loss, particularly those receiving cochlear implants. Research shows that the earlier a child receives a cochlear implant and begins rehabilitation, the better their language development and communication skills will be. This is crucial for academic success, social integration, and overall quality of life.
Goals of Early Intervention:
- Access to Auditory Listening: Supporting children in developing sound awareness and processing skills.
- Language Development: Developing spoken language skills through consistent auditory input.
- Communication Skills: Encouraging effective communication with peers and adults.
- Social Integration: Assisting children in connecting with their peers and participating in community activities.
- Equipping for Education: Preparing children for academic success through tailored support.
The Role of Teletherapy in Rehabilitation
Empowering Young Minds: Teletherapy Support for Children with Cochlear Implants
Teletherapy offers an accessible, flexible, and effective approach to rehabilitation for children with cochlear implants. By providing remote access to speech-language pathologists (SLPs) and other professionals, teletherapy can complement traditional face-to-face therapy, ensuring children receive consistent support and intervention.
Benefits of Teletherapy:
- Accessibility: Reaches children in remote or underserved areas.
- Convenience: Families can participate in sessions from home, reducing travel time and costs.
- Flexibility: Allows for more frequent sessions based on family needs.
- Parental Involvement: Engages parents actively in their child’s development, reinforcing skills learned during therapy.
Enhancing Communication Skills through Teletherapy
Teletherapy effectively addresses multiple communication skills in children with cochlear implants, focusing on areas such as auditory processing, speech articulation, and language understanding. Here’s how teletherapy can improve these skills:
Focus Areas for Teletherapy:
- Listening Skills: Activities designed to enhance auditory discrimination and sound awareness. This may include using engaging auditory games, music, or environmental sounds during sessions.
- Speech Production: SLPs can provide real-time feedback on articulation and voice quality, helping children refine their speech clarity and expression.
- Language Comprehension: Teletherapy can incorporate interactive storytelling, vocabulary building, and comprehension exercises, making learning engaging and fun.
- Communication Skills: Tailored activities that help children connect verbally with peers and adults.
Strategies for Successful Teletherapy Implementation
To enhance the efficacy of teletherapy for children with cochlear implants, it’s essential to implement several key strategies:
Technology Utilization:
- Video Conferencing Platforms: Utilizing user-friendly platforms like the XceptionalLEARNING Platform to conduct sessions, ensuring both parties can see and hear each other. This platform is designed specifically for therapy services, providing features tailored to the needs of children with cochlear implants.
- Interactive Tools: Employing digital tools such as the Digital Activity Book and other resources available on the XceptionalLEARNING Platform. These tools promote engagement and interaction during sessions, offering interactive exercises that support listening, speech production, and language comprehension in a fun and engaging way.
Individualized Therapy Plans:
- Customized Goals: Develop personalized therapy goals based on each child’s unique needs, strengths, and challenges.
- Continuous Assessment: Regularly monitoring progress and adjusting goals as needed to ensure ongoing development.
Engaging Content
- Use of Multimedia: Incorporating videos, songs, and animations to keep sessions engaging.
- Child-Centric Activities: Designing activities around the child’s interests to boost motivation.
Encourage Family Involvement
- Parent Training: Offering parents strategies to reinforce skills at home.
- Shared Activities: Including families in shared activities to strengthen the parent-child bond and therapeutic experience.
Obstacles in Teletherapy for Children with Cochlear Implants
Though teletherapy provides many advantages, it also brings challenges that need to be tackled:
Technical Barriers
- Access to Technology: Not all families have reliable internet or devices.
- User Familiarity: Some families may need training to effectively use teletherapy platforms.
Engagement and Motivation
- Maintaining Attention: Young children may have difficulty staying focused, requiring creative, interactive approaches.
- Home Distractions: Encouraging a dedicated therapy space can help reduce interruptions.
The Future of Teletherapy for Cochlear Implants
As technology continues to advance, the future of teletherapy for children with cochlear implants holds great promise:
- AI Integration: AI can tailor therapy activities to each child’s progress, ensuring a highly personalized experience.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Teletherapy encourages collaboration among SLPs, audiologists, educators, and families, providing comprehensive support for children.
- Broader Acceptance: As teletherapy becomes more accepted, training opportunities for SLPs and professionals in this area will expand, solidifying it as a standard practice.
In conclusion, teletherapy has emerged as a transformative tool for enhancing outcomes in children with cochlear implants, providing accessibility, flexibility, and targeted interventions. MERF-ISH (MERF – Institute of Speech & Hearing), a leading center in the field of auditory rehabilitation, plays a pivotal role in cochlear implant services. From pre-implant assessments to post-implant auditory-verbal therapy, MERF-ISH is at the forefront of integrating innovate technology and clinical expertise. Their comprehensive approach includes advanced audiological diagnostics, speech-language evaluations, and personalized rehabilitation plans that maximize the auditory potential of each child. By incorporating teletherapy, MERF-ISH is extending its specialized care to families beyond geographic limitations, ensuring that children receive continuous support for speech and language development, ultimately leading to improved social integration and academic success.











